What is DevOps: A Complete Overview

The acronym for the blend of development and operations is DevOps. It refers to a collective method that helps an organization’s Application Development team and IT Operations team to work together effortlessly and with enhanced communication. DevOps is a practice that promotes software development and operations teams to communicate, collaborate, integrate, and automate.
- DevOps is a set of cultural practices, concepts and technologies that improve an organization’s capacity to produce high-velocity application services and allow it to evolve and improve products faster than traditional software development and infrastructure management methods. As a result, organizations can better serve their clients and compete in the market because of this quickness.
- It is a mindset that boosts iterative software development, automation, and the deployment and management of programmable infrastructure. DevOps concentrates on developing trust and improving communication between developers and system administrators. DevOps is a software development method that tries to increase how businesses can deliver new features.
- DevOps fosters better, more constant communication, cooperation, visibility, integration and transparency between application development teams (Dev) and their IT operations counterparts (Ops).
- Every phase of the DevOps lifecycle is infused with this closer link between “Dev” and “Ops,” from early software planning to code, build, test, and release phases, deployment, operations, and continuous monitoring. In addition, this relationship fuels a never-ending cycle of advancement, expansion, testing, and deployment based on consumer feedback. As a result of these efforts, essential feature modifications or additions may be released more quickly and frequently.
How is DevOps used?
DevOps is a culture, technique, and collection of technologies that help developers, testers, and IT operations work together more effectively. It is a software delivery, quality, and innovation approach created and used by IT professionals, developers and business leaders to improve an organization’s software’s speed, quality, and innovation. DevOps is also about removing organizational hurdles that impede teams from properly collaborating. As a result, DevOps is becoming an essential element of most operations.
DevOps enables businesses to deliver more value to both internal (such as other departments) and external (such as customers) customers (such as end-users). Netflix, Google (Google Cloud), Facebook, Capital One, and many other corporations have implemented DevOps in their development processes, which has allowed them to scale quickly while keeping all operations secure.
DevOps Culture
DevOps is a shift in mindset. There is no more to say. It’s not just a matter of implementing agile planning, automated testing, or continuous delivery; these are all crucial techniques.
DevOps culture is all about operators and operators working together and sharing responsibility for the product they make. Enhancing transparency, communication, and collaboration across development, IT/operations, and “the business” is one way. DevOps culture entails closer collaboration and shared ownership for the products that development and operations generate and maintain. This allows businesses to align their people, processes, and tools to focus on consumers.
It entails forming multidisciplinary teams responsible for a product’s whole lifecycle. DevOps teams work independently and pursue a software engineering culture, methodology, and toolkit that prioritizes operational needs alongside architecture, design, and development.
The developers who built it also run it bringing them closer to the user and allowing them to understand their requirements and needs better. In addition, when operations teams are more involved in the development process, they can include maintenance and customer requirements, resulting in a better product.
Increased openness, communication, and collaboration amongst teams formerly performed in silos are at the core of DevOps culture. However, critical cultural transformations are required to bring these teams closer together. DevOps is a transformation in corporate culture that prioritizes continuous learning and improvement, mainly through team autonomy, quick feedback, high empathy and trust, and cross-team collaboration.
Practices in DevOps
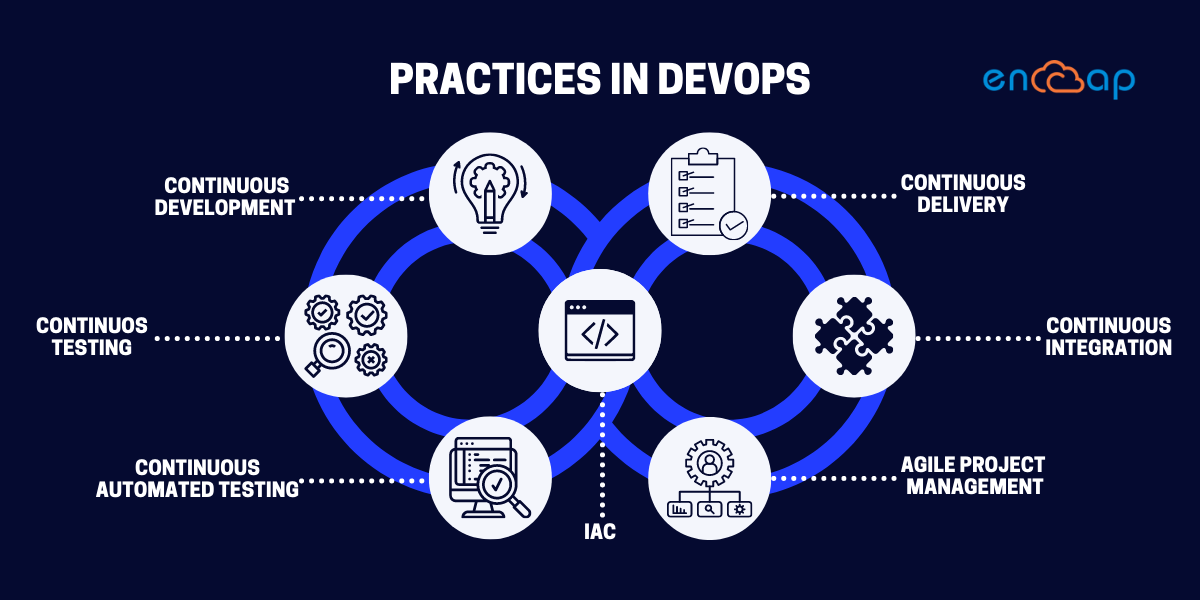
Continuous improvement and automation are crucial to DevOps approaches. As a result, many methods concentrate on one or more stages of the development cycle. The principles of DevOps are being executed in 83 per cent of IT decision makers’ organizations.
These are some of the practices:
Continuous development
This approach covers the planning and coding phases of the DevOps lifecycle. In addition, version-control techniques may be involved.
Continuous testing
This method incorporates automated, prescheduled, ongoing code tests as application code is produced or modified.
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is a development technique that requires developers to integrate work into a shared repository often and receive immediate feedback on its success.
The ultimate goal is to produce small, usable portions of code that are frequently checked and incorporated back into the centralized code repository.
Continuous Delivery
Every update to source code should be ready for a production release as soon as automated testing confirms it.
This includes building, testing, and deploying software automatically. To ensure that code can be deployed in an automated form with suitable pauses for approval depending on the individual demands of a programme, an approach to code approval and delivery approval must be in place.
Infrastructure as code
Infrastructure as code (IaC) is a method for managing the infrastructure that enables continuous delivery and DevOps.
It comprises scripts to set the deployment environment (networks, virtual machines, and so on) to the required configuration regardless of its starting condition.
Agile project management
Agile project management and software development is an iterative approach that aids teams propose value to clients faster and with fewer headaches. Instead of waiting for a single effective release date, agile teams concentrate on providing work in smaller increments. In addition, continuous evaluation of requirements, plans, and results allows teams to adapt to input and pivot.
Continuous automated testing
A quality assurance team uses automation tools like Selenium, Ranorex, and UFT to perform committed code testing. Bugs and vulnerabilities that are found are reported to the engineering staff. This step also includes a version control system to track changes to files and share them with other team members regardless of their location. In addition, automation is used to relieve the load of manually conducting repetitive tests, speed up the testing process, and allow the execution of more complicated or challenging tests.
Lifecycle of DevOps

DevOps represents an agile relationship between development and operations. It is a process practiced by the development team and operational engineers from the beginning to the final stage of the product. The DevOps lifecycle is a collection of phases that include continuous software development, integration, testing, deployment, and monitoring. A competent DevOps lifecycle is required to produce higher-quality software across the system.
Continuous development
This phase entails the software’s planning and coding.
During the planning phase of the DevOps lifecycle, the project’s vision is decided.
And the programmers get to work on the application’s coding.
There are no DevOps tools necessary for planning. However, there are several tools available for code maintenance.
Continuous integration
This is the most critical stage in the DevOps lifecycle. For example, a software development practice demands developers to commit source code changes more frequently. This could be done once a day or once a week. Then each commit is created, allowing for early discovery of any errors that may exist.
Compiling code entails unit testing, integration testing, code review, and packaging, but it also involves unit testing, integration testing, code review, and packaging.
Jenkins is a widely used tool in this phase. Jenkins gets the new code and prepares a build of it, an executable file in the form of war or jar, whenever there is a change in the Git repository.
Continuous testing
The testing step of the DevOps lifecycle follows, in which the developed code is examined for defects and mistakes that may have crept into the code. This is where quality analysis (QA) comes in handy for ensuring that the generated software is usable. The QA process must be conducted successfully to decide whether the software fits the client’s needs.
Continuous testing is accomplished with automation technologies like JUnit, Selenium, and TestNG, which enable the QA team to explore multiple codebases simultaneously. This assures that the generated programme has no defects in terms of functionality.
Continuous monitoring
The code is continuously integrated with the current code after being tested. Monitoring is a component of the DevOps approach that contains all operational elements, where vital information about the software’s use is recorded and carefully analyzed to uncover trends and pinpoint issues.
Continuous monitoring is an operational phase whose goal is to improve the software application’s overall efficiency.
Continuous feedback
Continuous feedback is necessary for determining and analyzing the application’s conclusion. It establishes the tone for enhancing the current version and launching a new version in response to stakeholder feedback. Only by assessing the results of software operations can the overall app development process be enhanced. Information acquired from the client’s end is referred to as feedback.
Information is essential in this case because it contains all of the facts on the software’s performance and related difficulties.
It also includes suggestions from the software’s users.
Continuous deployment
The code is forced to the production servers at this phase.
It is also vital to check that the code is correctly implemented. New code is regularly released, and configuration management solutions are essential for completing tasks often and quickly. Chef, Puppet, SaltStack and Ansible are the most common tools used in this phase. During the continuous deployment phase, containerization tools are also essential. Famous tools for this purpose include Vagrant and Docker, which aid in generating consistency throughout the development, staging, and testing environments.
Continuous operations
The final level of the DevOps lifecycle is the simplest to grasp.
Continuity is at the core of all DevOps operations, allowing developers to automate release procedures, spot errors promptly, and create better versions of software products.
Continuity is essential for avoiding detours and other unnecessary steps that hinder development. Continuous operations have quicker development cycles, allowing companies to advertise more frequently and reduce the overall time to market. DevOps adds value to software goods by making them better and more efficient, attracting new consumers.
Benefits of DevOps

DevOps is a more holistic approach to software development in which the development and operations teams collaborate on the project. As a result of faster feedback loops and more frequent delivery of updates and additions, the software development life cycle is shortened.
Maintain a stable working environment
Do you realize that the stress associated with delivering new features, repairs, or upgrades can destabilize your workspace and decrease overall productivity? With DevOps methodology, you can enrich your work environment by taking a consistent and well-balanced approach to operations.
High productivity is a result of transparency.
This approach allows for simple communication among team members by eliminating silo(ing) and promoting collaboration, focusing more on their specialized sector. As a result, integrating DevOps practices has increased productivity and efficiency among a company’s personnel. According to a DevOps trends survey in 2020- 99% of respondents expressed that DevOps has had a favorable influence on their organization.
Enhancement of innovation
By enabling teams to learn more and better understand client expectations, DevOps fosters innovation. Brainstorming multiple viewpoints and bouncing ideas off one other is a common way for people to develop new ideas. In addition, DevOps cultivates and supports an environment where rigid guidelines do not bind developers. This indicates that every project’s scope is always subject to change as long as the final results are satisfying.
Improvement in customer satisfaction and experience
The primary motivation for businesses to implement DevOps is to provide high-quality services to consumers or end-users faster. The most straightforward approach to keeping ahead of the competition is to focus on benefits that revolve around good customer service and improved income.
Agility and efficiency can come from various sources, but what matters is deepening customer connection at the end of the day.
Modern customers want a better experience across all digital platforms and brand touchpoints. Issues can be recognized earlier in the development pipeline by focusing on collaboration between different teams and creating multiple feedback loops. As a result, time spent troubleshooting is minimized, and customer experience improves.
Enhancement in the company’s agility
It’s no secret that being agile in your business can help you remain ahead of the competition. Due to DevOps, it is now possible to get the scale required to alter the business. DevOps checks all of the boxes commonly thought to be subsets of agility, enabling firms to become more agile. DevOps approaches, for example, allow a company to be adaptable when it comes to balancing capacity in response to demand changes. In addition, it permits them to understand better how customers use the goods and their general preferences so that they can persist in providing valuable features. It also enables the management of features and needs for several apps running on various platforms.
Improvement in collaboration and communication
DevOps entails a significant cultural transformation that eliminates communication barriers and allows people to cooperate and share resources freely—avoiding finger-pointing and enabling trust and collaboration by coordinating several teams to become cooperative. Consider how many problems could be solved by teams working independently rather than following a formal chain of command.
Facilitation of reliability and quality
For apparent reasons, the quality of your software is necessary, and DevOps may help you in maximizing that quality.
DevOps alters the way companies conduct traditional software testing. It boosts testing to a fundamental component of the SDLC, delegating responsibilities to all engineers involved.
It encourages exploratory testing, which can improve software quality by identifying practical ways to test various elements of completed software. Another crucial takeaway from a solid DevOps methodology is service dependability. Reliability refers to a system’s capacity to operate consistently within its environmental limits.
Conclusion
DevOps is a collaborative method that brings together an organization’s development and operations teams. DevOps is not solely a process or a collection of technologies.
DevOps is a mindset that alters how different teams in an organization collaborate to achieve business objectives.
If your company hasn’t yet adopted DevOps practices, you should seriously consider doing so. Regardless of what is holding you back, the benefits of DevOps are too great to ignore. Our service offerings at Encaptechno can assist you in determining practices that deliver value in the most innovatively and cost-effectively way possible. In addition, our team at Encaptechno will be happy to assist you in implementing them to get started with DevOps and help you achieve DevOps maturity.
What is DevOps: A Complete Overview Read More »
Cloud Services





